Bone marrow
is a spongy tissue found inside bones. The
bone marrow in the breast bone, skull, hips,
ribs and spine contains stem cells that produce
the body's blood cells. These blood cells
include white blood cells (leukocytes), which
fight infection; red blood cells (erythrocytes),
which carry oxygen to and remove waste products
from organs and tissues; and platelets, which
enable the blood to dot.
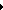 Bone marrow is the tissue found inside the
bone that produces red blood cells, white
blood cells and platelets. These essential
blood cells fight infection, carry oxygen
and help control bleeding. Any disease that
attacks the bone marrow can destroy the body's
ability to protect itself.
Bone marrow is the tissue found inside the
bone that produces red blood cells, white
blood cells and platelets. These essential
blood cells fight infection, carry oxygen
and help control bleeding. Any disease that
attacks the bone marrow can destroy the body's
ability to protect itself.
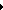 A bone marrow or stem cell transplant allows
a patient to receive high doses of chemotherapy
or radiation therapy to kill diseased cells
and make room for new, healthy cells.
A bone marrow or stem cell transplant allows
a patient to receive high doses of chemotherapy
or radiation therapy to kill diseased cells
and make room for new, healthy cells.
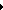 A stem cell transplant is used to treat many
diseases. First, the patient is given radiation
and/or chemotherapy to kill their diseased
cells. Then, donor stem cells are given to
the patient through a vein. This looks like
a blood transfusion. The transplanted donor
cells begin to grow in the patient to make
healthy red blood cells, white blood cells
and platelets necessary to support life.
A stem cell transplant is used to treat many
diseases. First, the patient is given radiation
and/or chemotherapy to kill their diseased
cells. Then, donor stem cells are given to
the patient through a vein. This looks like
a blood transfusion. The transplanted donor
cells begin to grow in the patient to make
healthy red blood cells, white blood cells
and platelets necessary to support life.
|